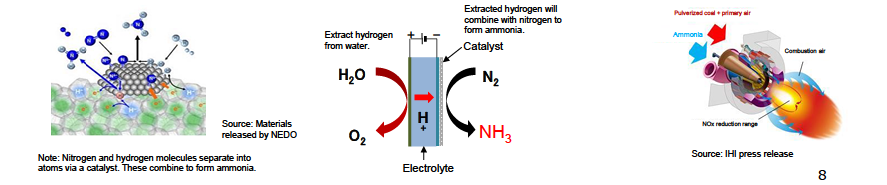
Agency for Natural Resources and Energy METI, Japan
Fuel Ammonia: Production and utilization processes
- Ammonia does not emit CO2 during combustion and becomes one of the effective fuels for combating global warming. It can be produced from natural gas (fossil fuels) with CO2 offset, or renewable energy.
- Ammonia is not only positioned as one of the hydrogen carriers, but also be used directly for electricity generation as a zero emission fuel.
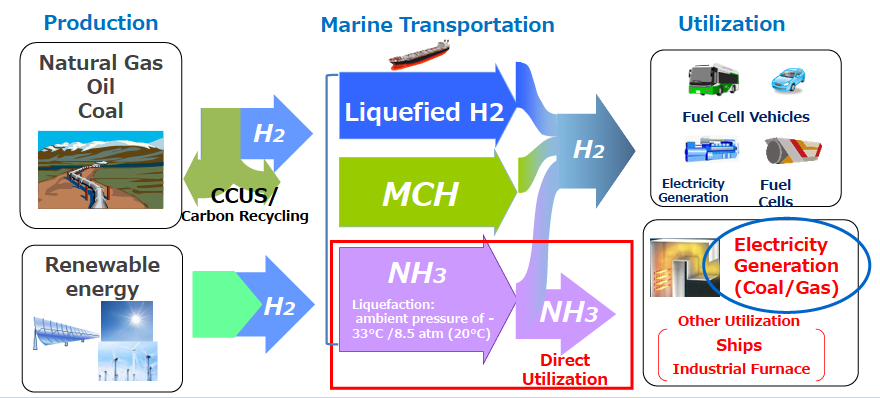
What is ammonia co-firing in thermal power plants?
- Ammonia co-firing means replacing some of the coal used for combustion with ammonia.
- It has an advantage that existing coal-fired power plants can be converted into ammonia co-firing plants at low cost with a relatively small-scaled modification.
- It can be said that 50% and more co-firing means ammonia power generation with fossil fuel co-firing.
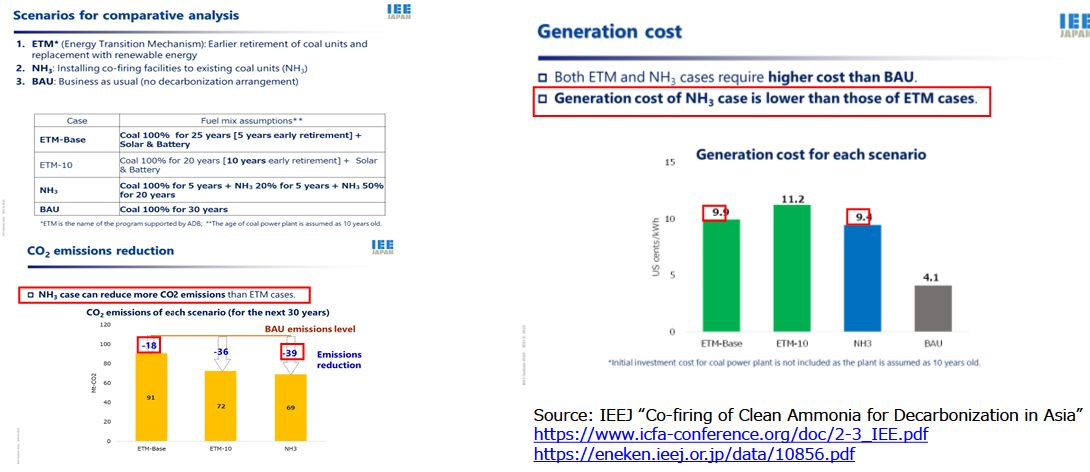
The effectiveness of ammonia co-firing especially in Asia : IEEJ report
- Many coal-fired power plants in Asia are still young, and many more are under construction.
- Ammonia co-firing (NH3-case) emits 39 Mt-CO2 lower than BAU emissions level, while Early Transition Mechanism (Earlier retirement of coal units and replacement with renewable energy)-Base case does 18 Mt- CO2 lower than BAU emissions level for the next 30 years. In addition, generation cost of NH3-case (9.4 US cents/kwh) is lower than that of ETM-Base case (9.9 US cents/kwh).
- Ammonia co-firing is an effective and realistic option to decarbonize the existing coal-fired power plants in Asia.
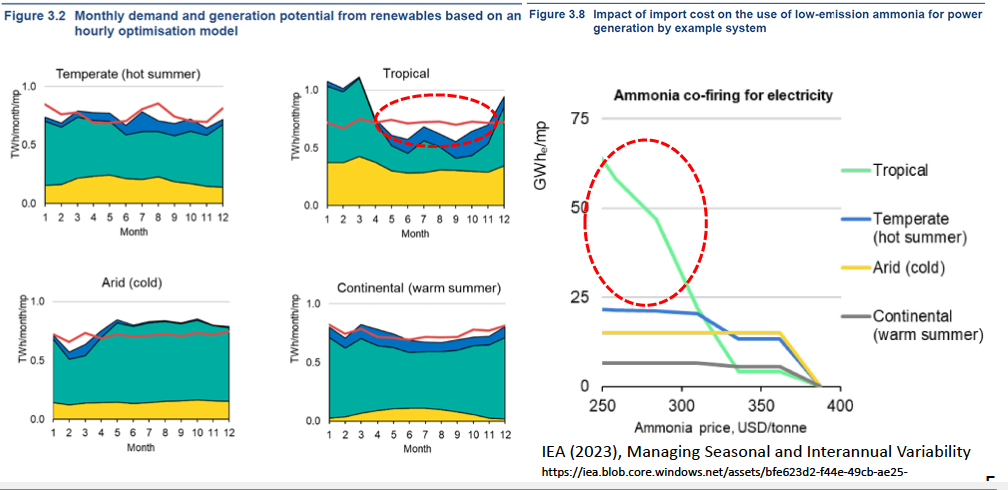
The effectiveness of ammonia co-firing especially in Asia : IEA report
- Daily variation of renewable can’t manage seasonal and interannual variability, even with batteries. Along with increase of renewables, flexibility provided by thermal power plants will take an essential role to maximum utilization of renewables with stable electricity supply, even if utilizing hydro power.
- Hydrogen/Ammonia for the power sector is important in Tropical including SE Asia.
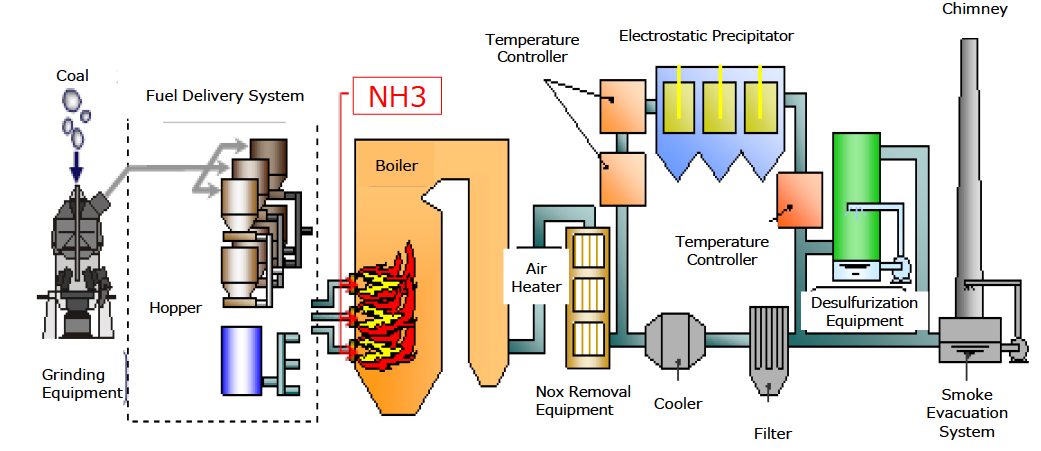
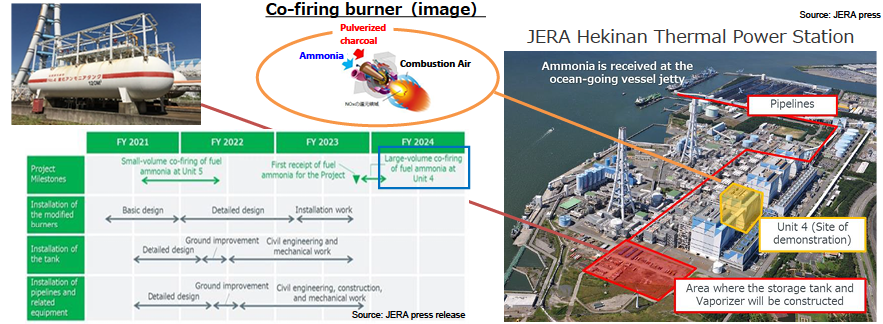
Ammonia co-firing into existing coal-fired power plants
- As Japan’s original technology, stable combustion and reduced NOx emissions with 20% of ammonia co- firing have been already achieved. The demonstration with actual large-scale equipment (1GW power plant) is going to start in 2023FY and is expected to be completed in 2024FY.
- To achieve zero-emission thermal power plants, high ratio (50%-) co-firing burners will be developed by 2023FY and single-fuel firing burners will be developed by 2024FY in the test furnace respectively. Large-scale demonstration will be completed in 2028FY through Green Innovation Fund.
Ammonia firing into gas-fired power plants
- Ammonia firing can be applied not only to coal-fired power plants, but also to gas-fired power plants.
- Ammonia single-fuel firing has already successfully been acheived with 99% GHG reduction (without NOx emissions) at a 2MW-class gas turbine, and the development of ammonia single-fuel firing at 40MW-class gas turbine will be commercialized around 2025.

Technology Development for the Utilization of Ammonia
|
Ammonia synthesis technology |
|
Green ammonia synthesis | High ratio co-firing and single-fuel firing burners | |
|
(Chiyoda Corporation, JERA, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Subcontractor: Tsubame BHB, etc.) In order to reduce blue ammonia synthesis costs (operating costs by more than 15%), develop technology that can synthesize it at lower temperatures and pressures than the Haber–Bosch process. |
|
(Idemitsu, The University of Tokyo, Kyushu University, Osaka University, Tokyo Institute of Technology)
|
|
(IHI, Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, JERA, Tohoku University, National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology)
|